Security
Into the Dark Web
If you are thinking “I’ve heard of the dark web, but I don’t really know what it is,” well, I am here to shed some light on the mysteries of the dark web.
The term Internet is often used interchangeably with the term web. In reality, they are separate components of an ecosystem. The Internet is the infrastructure and network that allows people and systems from all over the world to communicate with each other. This includes the network, switches, routers, etc. that interconnect all the devices. The web is one service that leverages the Internet but there are many others. The World Wide Web (www) is the service that allows a browser (Edge, Chrome) to connect and interact with a web server. Streaming services (Netflix, BritBox), conferencing services (Teams, Zoom), file sharing services (OneDrive, Google Drive) are other services commonly using the Internet.
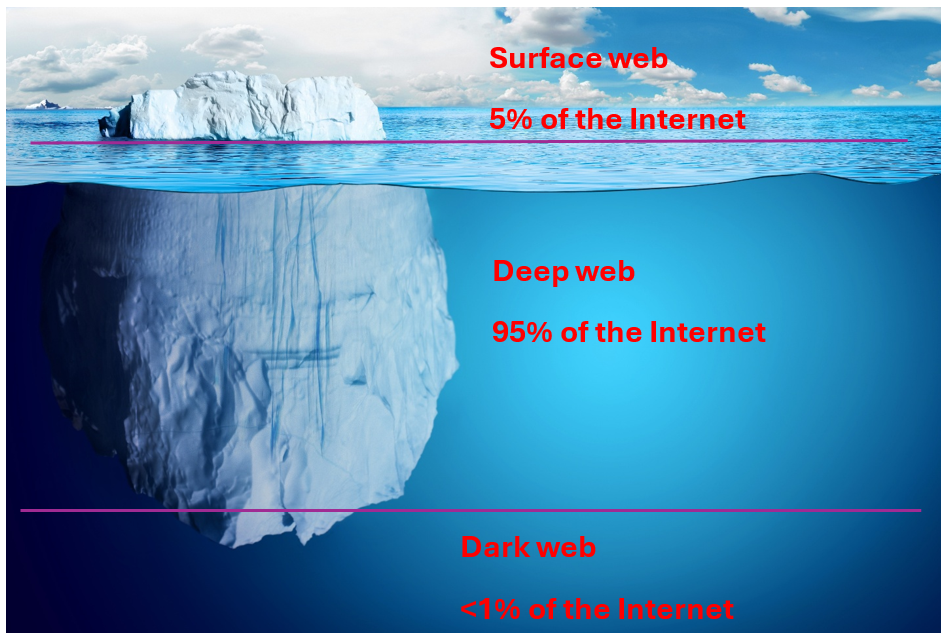
There are essentially three webs: surface, deep, and dark.
Surface Web
The surface web is the one openly available on the Internet. It is the one most people think of when referring to the web. Search engines such as Google and Bing discover and index all publicly available sites allowing people to find the sites for which they are searching.
Deep Web
The deep web is essentially the opposite of the surface web. It comprises the sites and content that are not publicly available and hidden, i.e. the content that is not indexed. This is the content where you need to be granted access to see it. If you think about it, this makes sense. You need a Netflix account to stream their content. You need a Facebook account to view posts. What is public is the fact that the site exists, the login page, and information on how to obtain access. To put some numbers around the size of the deep web, it is 95% of all content on the Internet.
Dark Web
The dark web is a small fraction of the deep web, comprising of about .01% of the Internet. The surface web is the tip of the iceberg. The vast majority of the iceberg is below the water, representing the deep web. The dark web is the content at the very bottom, which is the most secluded part of the iceberg.
The dark web is a portion of the internet that is intentionally hidden and requires specific tools to access. As a result, it provides anonymity, which lends itself well to illicit online activity.
Why do people perform this illicit activity? There are three common motivations why people may want to stray far from the straight and narrow:
- Financial – people that want to steal data to monetize it. These are the people that take credit card data, personally identifiable information (PII), and personal healthcare information (PHI) and are in it for a buck (or quid for those of you on the other side of the pond). Megacart, FIN7, Lazarus Group, and Evil Corp are known for performing online financial crime.
- Hacktivism – people wishing to make a political or social statement by attacking sites. Groups such as Anonymous, LulzSec, and Cult of the Dead Cow are known for hacktivism.
- Cyberespionage – this is state-sponsored activity that benefits a country. China and Russia are commonly thought of for performing this activity.
What they all have in common is they need a way to communicate securely and a place to buy and sell their wares with a high degree of privacy. The dark web is the medium of choice; a marketplace of products and services used to carry out these motivations. You can buy drugs, hire people for services, purchase passports, and so much more that may not be considered legal in many jurisdictions. You can also check social media, get a weather report, and get directions to and from your office.
The Tor browser is used to surf the dark web and .onion sites are the pages with the content. .onion is the domain suffix for the dark web, so named because they operate like layers of an onion that you need to peel to get where you want to go. It makes connections by relaying through at least three random nodes (the layers of the onion). The nodes add and remove layers of encryption (more onion references) to keep each individual connection private. As you move from page to page, a new and unique path is established. This hides your true source and destination from anyone that may eavesdrop on your session. Only the last node in the path can be identified.
The Tor browser is based on Mozilla Firefox so it can also be used to browse the other webs as well. It doesn’t go the other way though, so a standard browser cannot be used to surf the dark web.
The currency of choice on the dark web is Bitcoin. It provides an anonymous way to exchange money, allowing for complete privacy in all aspects of operating on the dark web.
But there are legitimate uses for the dark web:
- Privacy Protection
- Journalists and activists use it to communicate securely in countries with heavy censorship or surveillance.
- Whistleblowers can share sensitive information anonymously.
- Access to Restricted Information
- People in regions with internet censorship can access blocked news sites or educational resources.
- Secure Communication
- Encrypted messaging services and forums allow individuals to discuss topics without fear of government or corporate monitoring.
- Research and Cybersecurity
- Security professionals monitor dark web marketplaces for stolen data or emerging threats.
- Companies use it to detect leaked credentials or intellectual property.
- Legal Anonymous Browsing
- Some users simply value anonymity for personal reasons (e.g., avoiding tracking by advertisers).
The dark web is a tool. Like any other tool, how it is used dictates if it is for good or bad. It is a tool that has no practical use for legitimate business purposes other than organizations that specialize in performing security research or investigations. It is recommended to block or prevent the use of the Tor browser in a corporate environment.
If you are personally curious, please be careful when surfing on the darkest of webs. Darkness makes it difficult to see things lurking in the shadows.
